Hand Anatomy
BONES
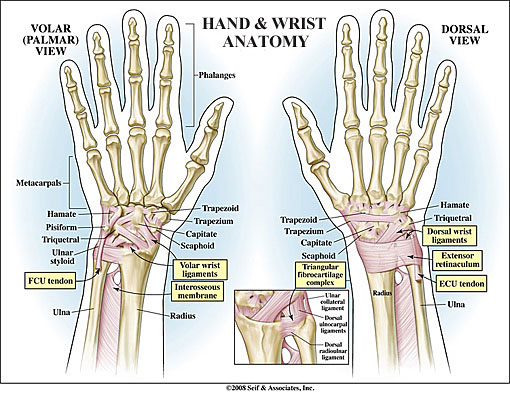
Metacarpals
The five bones that form the palm of the hand and connect to each digit.
Proximal Phalanges
The five cylindrical bones closest to the metacarpals that connect the five digits to the palm.
Middle Phalanges
The four cylindrical bones that make up the middle of the fingers. (The thumb does not have a middle phalanx.)
Distal Phalanges
The five cylindrical bones that form the tips of the fingers and thumb.
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
The rubbery, slippery substance that covers the ends of bones at the joint. Healthy cartilage enables smooth joint movement and absorbs shock.
JOINTS
Metacarpophalangeal Joint
The base knuckle joints that connect the metacarpal bones to the proximal phalanges.
Proximal Interphalangeal Joint
The middle knuckle joints that connect the proximal phalanges to the middle phalanges.
Distal Interphalangeal Joint
The top knuckle joints that connect the middle phalanges to the distal phalanges.
LIGAMENTS AND TENDONS OF THE HAND
Collateral Ligaments
Ligaments found on each side of each joint on the fingers and thumb that serve to prevent abnormal sideways bending.
Volar Plate
A strong ligament that connects the proximal to the middle phalanges on the palmar side of every joint of the hand and protects the fingers from hyperextension.
Extensor Hood
A broad sheet of interconnected tendons most prominent at the metacarpal-phalangeal joint of the finger that helps straighten the proximal, middle and distal phalanges.
MUSCLES
Intrinsic Muscles
The small muscles of the hand that serve to position and hold fingers steady during fine-tuned activity such as spreading the fingers.
Thenar Eminence
The muscles that form the spongy pad right below the thumb whose main function is opposition.
NERVES
Brachial Plexus
The brachial plexus is the nerve center at the root of the neck and shoulder which is comprised of portions of the nerve roots originating from the cervical spinal cord. This group of nerves criss-crosses and branches and supplies the muscles of the back of the shoulder, chest and the entire upper extremity to the fingertips.
Radial Nerve
One of three nerves originating at the shoulder that carry signals from the skin and joints to the brain and back again to the muscles of the upper extremities to coordinate movement and position sense. The radial nerve begins from the inside of the upper arm, travels diagonally across to the outer elbow and then again crosses to the thumb side of the forearm and into the back of the thumb, index and half of the middle finger. Muscles controlled by the Radial Nerve include the triceps and wrist and finger extensors.
Median Nerve
One of three nerves originating at the shoulder that carry signals from the skin and joints to the brain and back again to the muscles of the upper extremities to coordinate movement and position sense. The median nerve begins from the outside of the upper arm and travels down the inner side of the upper arm before moving to the center of the forearm and into the palmar side of the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger and distal segment of the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers. Muscles controlled by the Median Nerve include the wrist and finger flexors.
Ulnar Nerve
One of three nerves originating at the shoulder that carry signals from the skin and joints to the brain and back again to the muscles of the upper extremities to coordinate movement and position sense. The ulnar nerve begins from the inside of the upper arm and travels down the inside of the forearm and into the palmar and dorsal sides of the pinky and half of the ring finger. Muscles controlled by the Ulnar Nerve include the wrist and finger flexors, as well as the small muscles in the hand that coordinate fine movements.
BLOOD VESSELS
Ulnar Artery
The artery that travels near the ulnar nerve into the pinky side of the hand and joins the radial artery in the palm to provide blood to the front of the hand and fingers with branches spreading dorsally.
Radial Artery
The artery that travels across the front of the wrist on the thumb side of the hand and joins the ulnar artery in the palm to provide blood to the front of the hand and fingers with branches spreading dorsally.
BURSAE
Sacs containing lubricating fluid that serve to reduce friction between tendons and bones and skin and bones.



