Elbow Anatomy
BONES
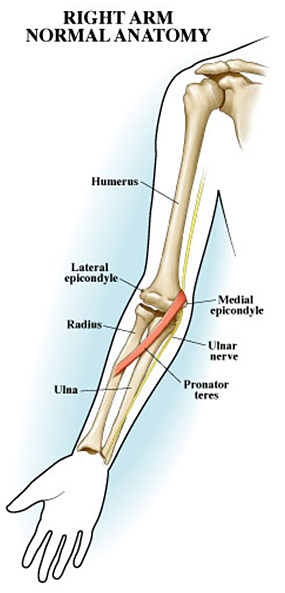 Ulna
Ulna
The longer of two forearm bones, located on the pinky side of the arm
Radius
The shorter of two forearm bones, located on the thumb side of the arm
Lateral Epicondyle
The outside bump just above the elbow where the tendons connecting muscles that straighten the fingers and wrist attach.
Medial Epicondyle
The inside bump just above the elbow where the tendons connecting muscles that bend the fingers and wrist attach.
ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
The rubbery, slippery substance that covers the ends of bones at the joint. Healthy cartilage enables smooth joint movement and absorbs shock.
LIGAMENTS AND TENDONS
Medial Collateral Ligament
One of two ligaments that connect the humerus to the ulna. The medial side refers to the position on the inside edge of the elbow.
Lateral Collateral Ligament
One of two ligaments that connect the humerus to the radius and ulna. The lateral side refers to the position on the outside edge of the elbow.
Annular Ligament
The ring-shaped ligament that wraps around the head of the radius and keeps it snugly in place against the ulna.
Distal Biceps Tendon
The tendon that attaches the biceps muscle at the front of the upper arm to the radius that allows the elbow to bend and supinate.
Distal Triceps Tendon
The tendon that attaches the triceps muscle at the back of the upper arm to the ulna that allows the elbow to straighten.
MUSCLES
Biceps
One of themuscles at the front of the upper arm that allows the elbow to bend and supinate.
Triceps
The muscle at the back of the upper arm that allows the elbow to straighten.
Wrist Flexors
The muscles attaching to the medial epicondyle and running down the front of the forearm that serve to flex the wrist and hand
Wrist Extensors
The muscles attaching to the lateral epicondyle and running down the back of the forearm that serve to extend the wrist and hand
NERVES
Radial Nerve
One of three nerves originating at the shoulder that carry signals from the skin and joints to the brain and back again to the muscles of the upper extremities to coordinate movement and position sense. The radial nerve begins from the inside of the upper arm, travels diagonally across to the outer elbow and then again crosses to the thumb side of the forearm and into the back of the thumb, index and half of the middle finger. Muscles controlled by the Radial Nerve include the triceps and wrist and finger extensors.
Median Nerve
One of three nerves originating at the shoulder that carry signals from the skin and joints to the brain and back again to the muscles of the upper extremities to coordinate movement and position sense. The median nerve begins from the outside of the upper arm and travels down the inner side of the upper arm before moving to the center of the forearm and into the palmar side of the thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger and distal segment of the thumb, index, middle and ring fingers. Muscles controlled by the Median Nerve include the wrist and finger flexors.
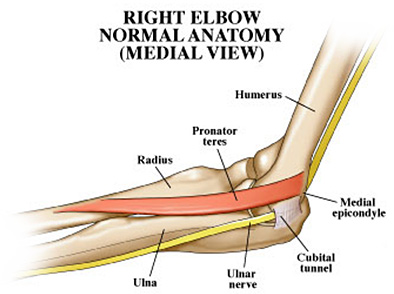
Ulnar Nerve
One of three nerves originating at the shoulder that carry signals from the skin and joints to the brain and back again to the muscles of the upper extremities to coordinate movement and position sense. The ulnar nerve begins from the inside of the upper arm and travels down the inside of the forearm and into the palmar and dorsal sides of the pinky and half of the ring finger. Muscles controlled by the Ulnar Nerve include the wrist and finger flexors, as well as the small muscles in the hand that coordinate fine movements.
BLOOD VESSELS
Brachial Artery
The main artery leading from the upper arm down to the front crease of the elbow, where it branches into the ulnar artery and radial artery.
Ulnar Artery
The artery branching off the brachial artery below the elbow that brings oxygenated blood down the pinky side of the forearm and into the wrist and hand.
Radial Artery
The artery branching off the brachial artery below the elbow that brings oxygenated blood down the thumb side of the forearm and into the wrist and hand.
BURSAE
Sacs containing lubricating fluid that serve to reduce friction between tendons and bones and skin and bones.